Overarching principles
Overarching principles
While at all times safeguarding the wellbeing of the child, the aims when providing dental care for children are:
- to prevent disease in the primary and permanent dentition
- to reduce the risk of the child experiencing pain or infection or acquiring treatment-induced dental anxiety if dental caries does occur
- for the child to grow up feeling positive about their oral health and with the skills and motivation to maintain it
To achieve these aims, the priorities for the dental team are:
- to involve both the child and their parent/carer in decisions regarding the child’s oral health care
- to encourage the child’s parent/carer to take responsibility for their child’s oral health, implement preventive advice at home and meet their responsibilities to bring their child for dental care
- to ensure that valid consent for planned treatment is obtained from the child and/or their parent/carer
- to relieve pain or infection, if present
- to apply preventive measures to the highest standard possible informed by an assessment of the child’s risk of developing caries
- to focus on prevention of caries in the permanent dentition before management of any caries in the primary dentition
- if caries in the permanent dentition does occur, to diagnose it early, and manage it appropriately
- to manage caries in the primary dentition using an appropriate technique that maximises the chance of the tooth exfoliating without causing pain or infection, while minimising the risk of treatment-induced anxiety
- to identify as early as possible those children where there is concern about a parent/carer’s ability to comply with dental health preventive advice, support or treatment uptake, and to contact and work collaboratively with other professionals (e.g. school nurse, general medical practitioner, Childsmile dental health support worker, health visitor or social worker)
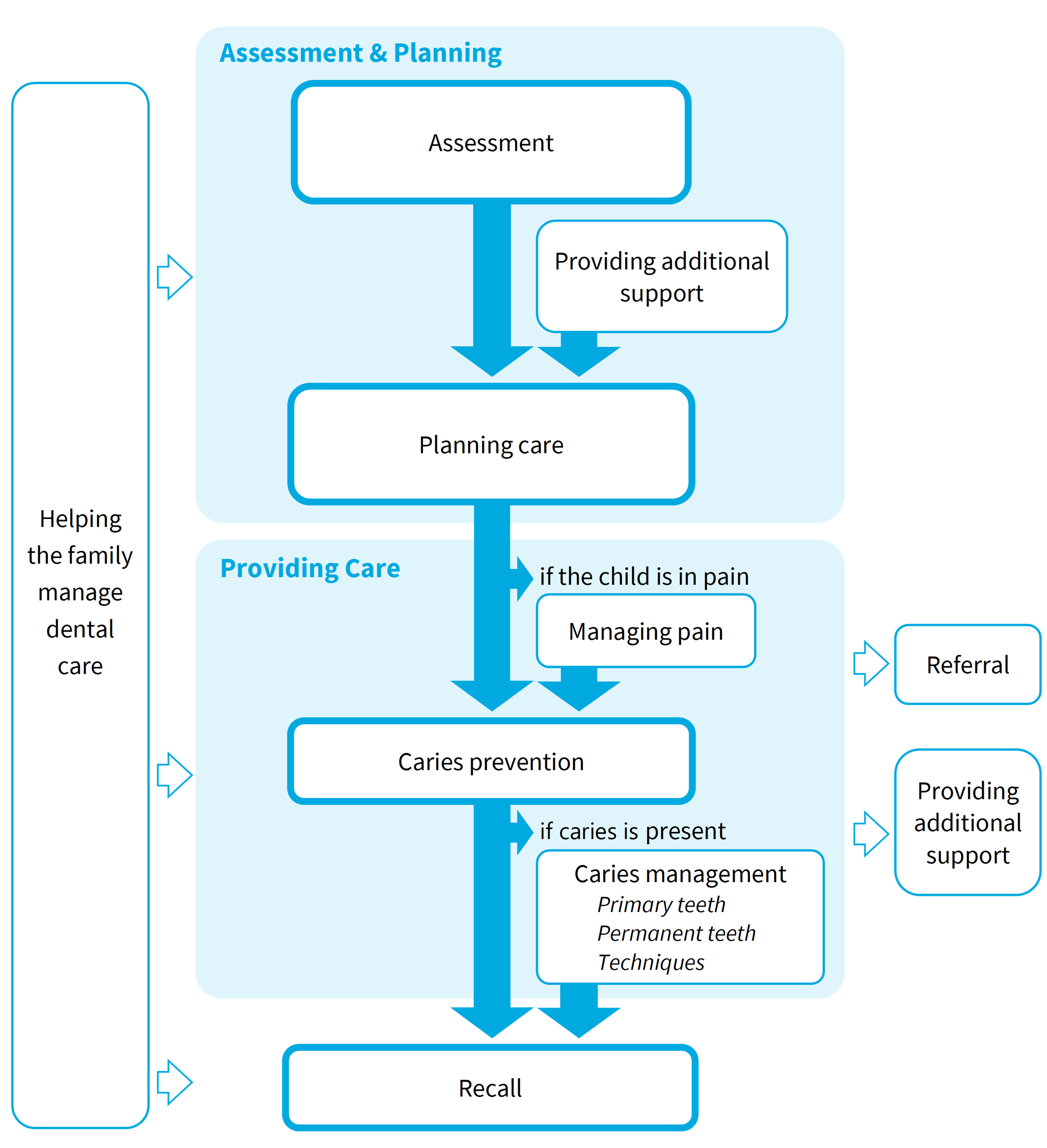
In practice, the prevention and management of dental caries in children comprises several elements. This is illustrated in the figure below, which emphasises that while some children may require additional support and pain and/or caries management, all children need caries prevention. This figure also serves as a route map for this guidance, indicating the sections that are concerned with each element of the prevention and management of dental caries in children.