Management of caries in primary teeth
Decision-making for managing the carious primary tooth in a child with no medical complications
This flowchart illustrates the key decisions to be made in forming an appropriate caries management plan that considers the factors that influence treatment provision. If a child is pre-cooperative or unable to co-operate (due to young age, a learning disability or where behaviour management techniques have been unsuccessful) or has multiple affected teeth, referral to assess suitability for extractions under sedation or general anaesthesia may be necessary (see Referral).
An accessible version is available and the flowchart is also included in the downloadable Guidance in Brief.
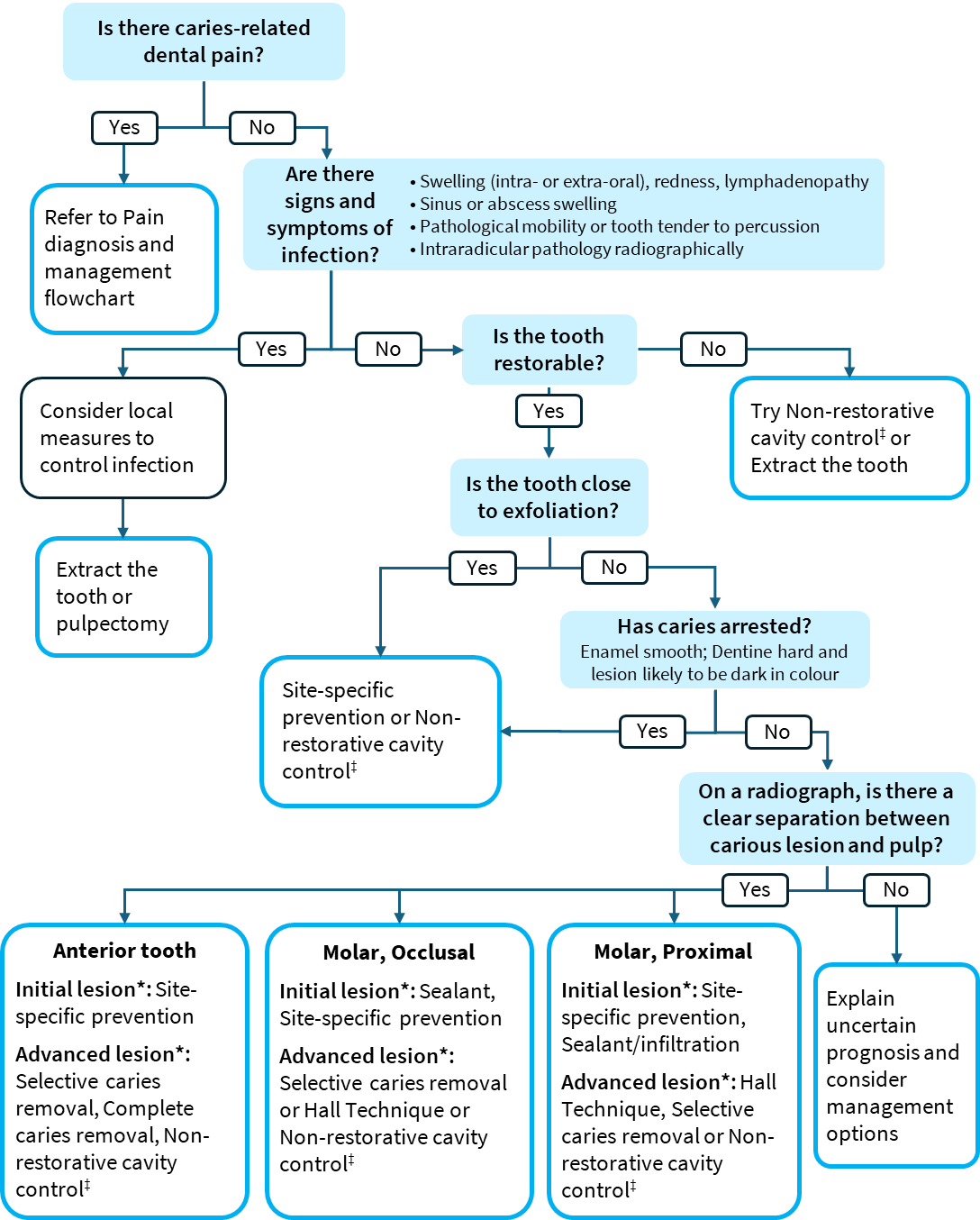
‡ Non-restorative cavity control includes making the lesion cleansable, supporting improvements in toothbrushing and diet, fluoride varnish application, silver diamine fluoride application.
* For descriptions of initial and advanced lesions in primary teeth, see Lesion classification.