Options for management of carious primary teeth
Management options for carious primary teeth when there are no clinical or radiographic signs of pulpal involvement
In a child with no medical complications, for each type of lesion when there are no clinical or radiographic signs of pulpal involvement, the preferred treatment option(s) are indicated √. Alternative options that may be appropriate in certain circumstances are indicated (√) with explanation in the footnotes. See Dental techniques for further details on each caries treatment technique. For a description of each lesion type, see Lesion classification.
An accessible version is available and the table is also included in the downloadable Guidance in Brief.
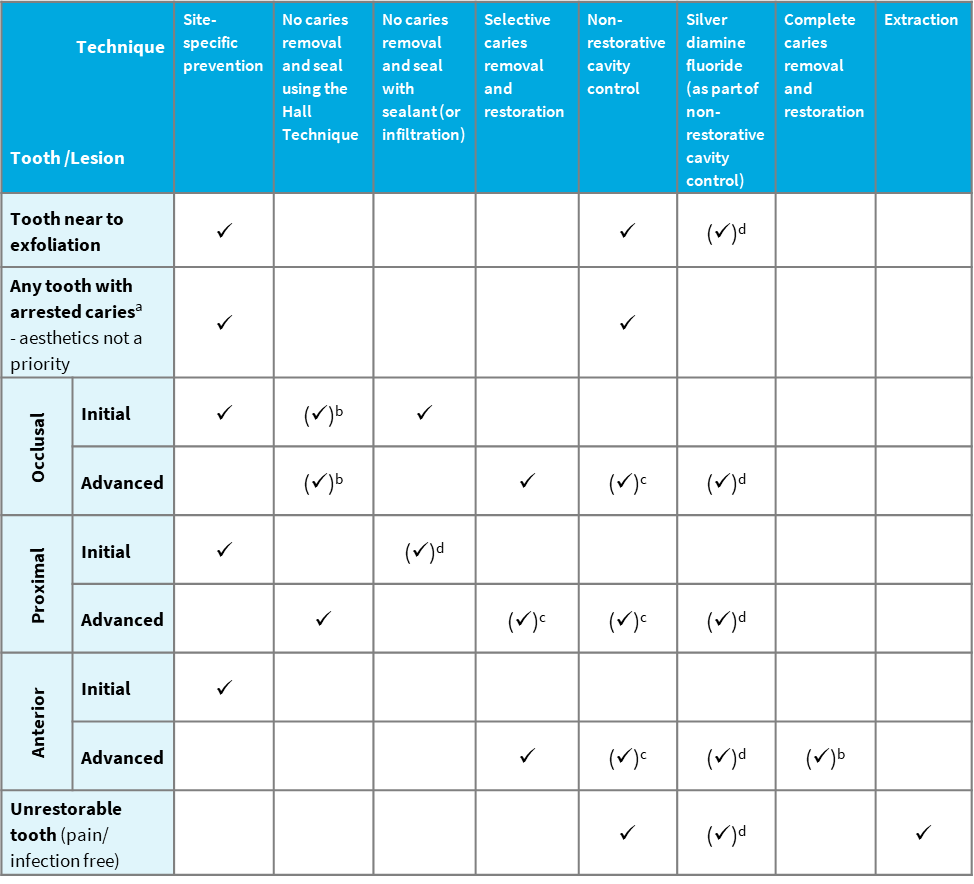
a Caries is considered to have arrested when there is demonstrable evidence of non-progression of lesions over several months using a recording system, such as photographs or ICDAS codes.
b For these lesions, other options are considered preferable.
c Due to a lack of supporting evidence, this approach is only appropriate for these types of lesions if no alternative is feasible. Document use of this approach and rationale in the patient’s record.
d Technique with a developing supporting evidence base.
Accessible version
To use this version, click on the chosen tooth or lesion to show the preferred and alternative treatment options.
Preferred treatment options:
or
Non-restorative cavity-control
Alternative treatment option:
Silver diamine fluoride (as part of non-restorative cavity control)d
d Technique with a developing supporting evidence base.
Preferred treatment options:
or
Non-restorative cavity-control
* Caries is considered to have arrested when there is demonstrable evidence of non-progression of lesions over several months using a recording system, such as photographs or ICDAS codes.
Preferred treatment options:
or
No caries removal and seal with sealant (or infiltration)
Alternative treatment options:
No caries removal and seal using the Hall Techniqueb
b For these lesions, other options are considered preferable.
Preferred treatment option:
Selective caries removal and restoration
Alternative treatment options:
No caries removal and seal using the Hall Techniqueb
or
Non-restorative cavity controlc
or
Silver diamine fluoride (as part of non-restorative cavity control)d
b For these lesions, other options are considered preferable.
c Due to a lack of supporting evidence, this approach is only appropriate for these types of lesions if no alternative is feasible. Document use of this approach and rationale in the patient’s record.
d Technique with a developing supporting evidence base.
Preferred treatment option:
Alternative treatment options:
No caries removal and seal with sealant (or infiltration)d
d Technique with a developing supporting evidence base.
Preferred treatment option:
No caries removal and seal using the Hall Technique
Alternative treatment options:
Selective caries removal and restorationc
or
Non-restorative cavity controlc
or
Silver diamine fluoride (as part of non-restorative cavity control)d
c Due to a lack of supporting evidence, this approach is only appropriate for these types of lesions if no alternative is feasible. Document use of this approach and rationale in the patient’s record.
d Technique with a developing supporting evidence base.
Preferred treatment option:
d Technique with a developing supporting evidence base.
Preferred treatment option:
Selective caries removal and restoration
Alternative treatment options:
Non-restorative cavity controlc
or
Silver diamine fluoride (as part of non-restorative cavity control)d
or
Complete caries removal and restorationb
b For these lesions, other options are considered preferable.
c Due to a lack of supporting evidence, this approach is only appropriate for these types of lesions if no alternative is feasible. Document use of this approach and rationale in the patient’s record.
d Technique with a developing supporting evidence base.
Preferred treatment options:
Non-restorative cavity control
or
Alternative treatment options:
Silver diamine fluoride (as part of non-restorative cavity control)d
d Technique with a developing supporting evidence base.